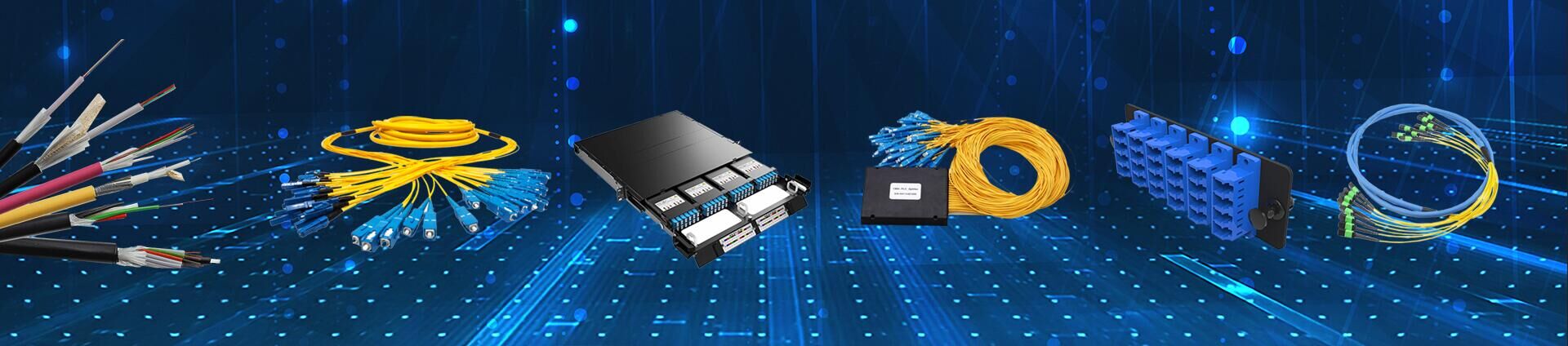
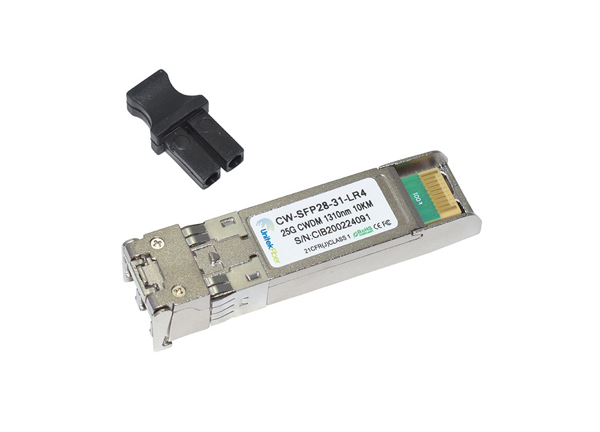
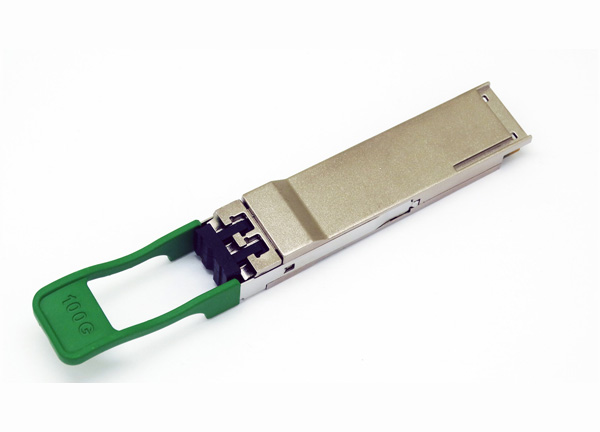
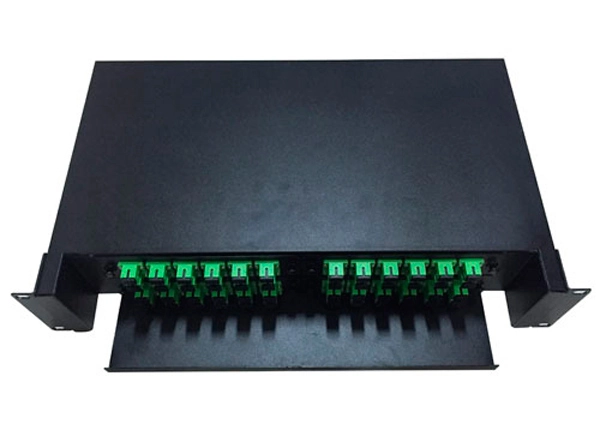
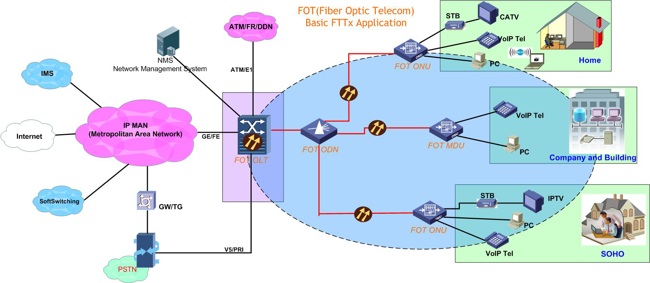
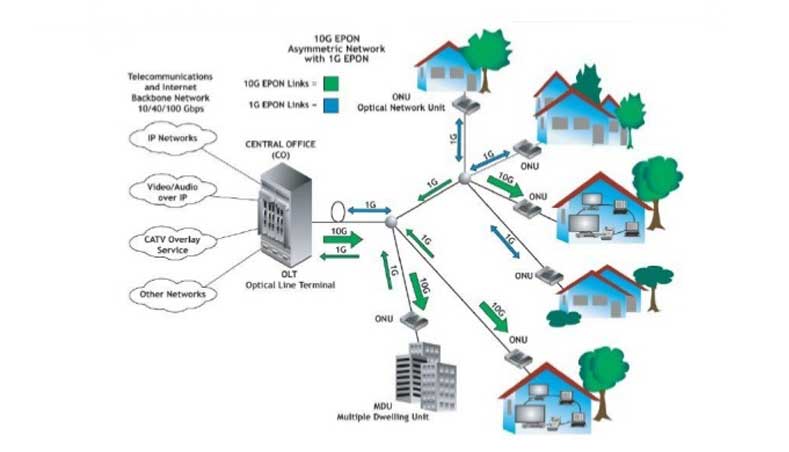
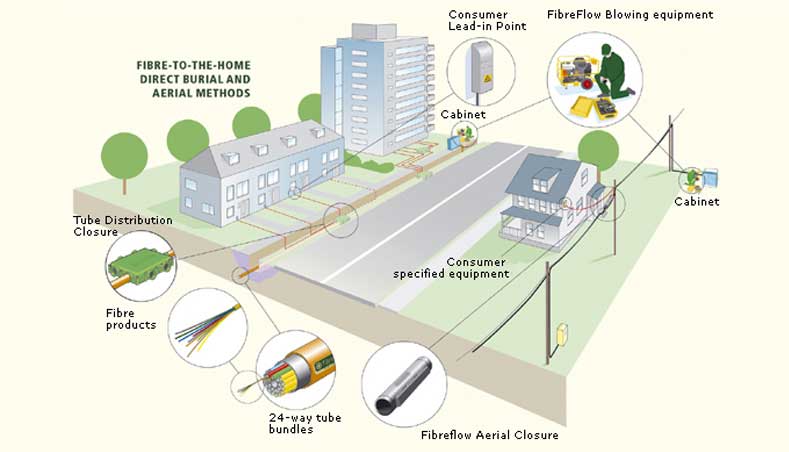
The central office equipment is the optical line terminal (OLT) and the customer equipment is the optical network unit (ONU) or Optical Network Terminal (ONT). According to the distance from the fiber to the user, FTTx technology can be divided into four service modes: Fiber To The Cabinet (FTTCab), Fiber To The Curb (FTTC), Fiber To The Building (FTTB) and Fiber To The Home (FTTH). US operator Verizon combines FTTB and FTTH with Fiber To The Premise (FTTP). The above services can be collectively referred to as FTTx.
The rapid development of HDTV, VOD, HIS and other services has become more and more demanding on bandwidth.
The optical access transmission distance is long, the coverage is large, and the site capacity is larger.
It provides high bandwidth for residents and small and medium business users.
Passive optical network between the central office and the user saves cost and improves reliability.
The use of fiber optic cable instead of copper cable greatly reduces equipment and maintenance costs and improves service quality.
The access medium evolves from copper wire to fiber, and the entire access layer optical network (ODN) needs to be modified to bring new market opportunities.
The legislative bodies of the United States and other countries have introduced the "Telecom Law", which has lifted the control of its domestic telecommunications market, and users can obtain low-cost and high-quality services.
Japan, South Korea, Singapore and other countries have issued a series of related bills to support the construction of broadband information in the country, which provides a great impetus for the development of FTTx network.