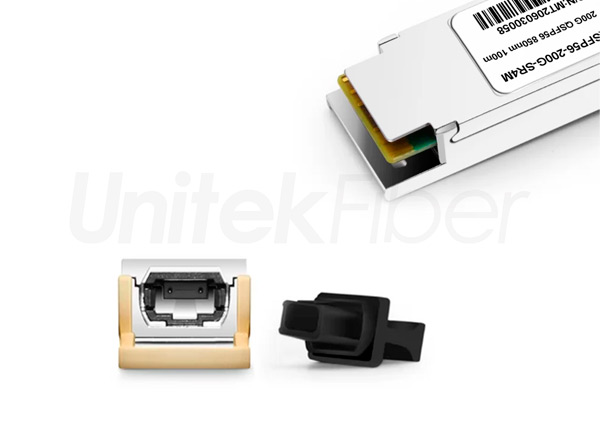
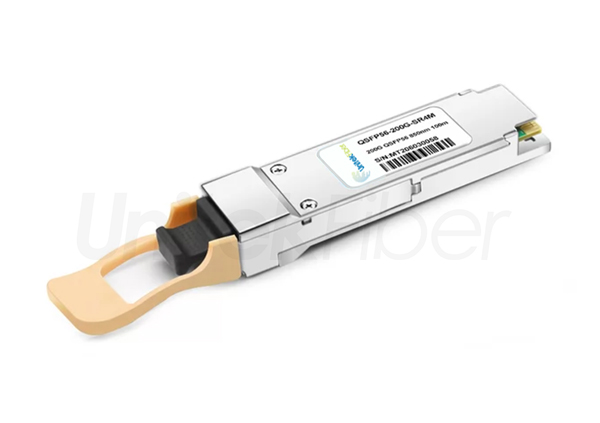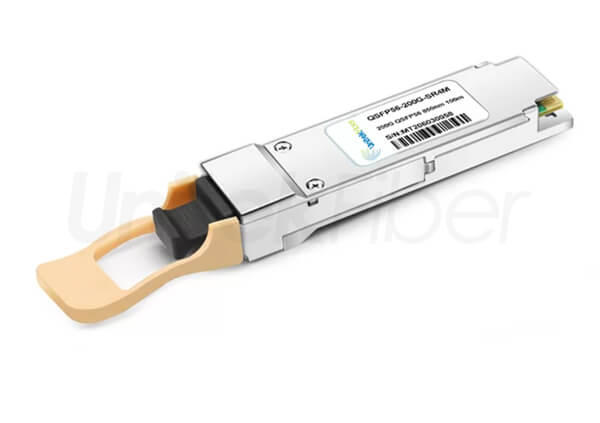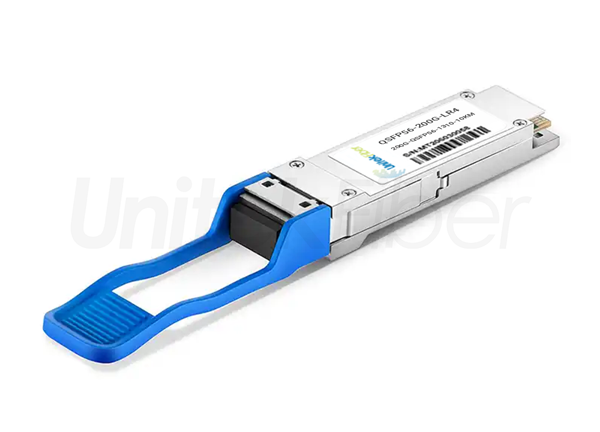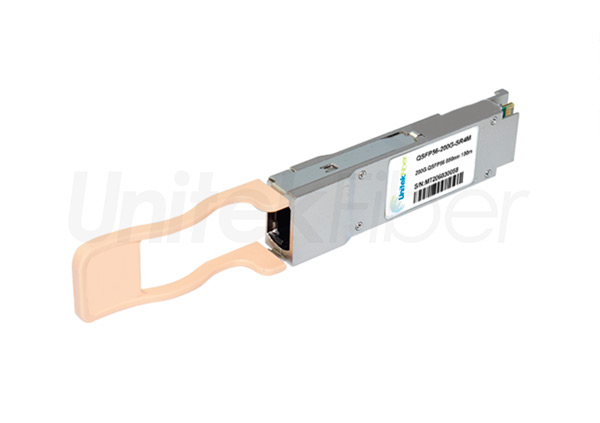









The 200G QSFP56 optical transceiver module is an upgraded version of the 40G QSFP+ and 100G QSFP28 optical transceiver modules. QSFP56 is designed for 200G Ethernet. The QSFP56 optical transceiver module is a four-channel hot-pluggable optical transceiver module with four transmit and receive channels. Each channel can run at a speed of 53.125 Gb/s and can support 4x50G transmission. The rate can reach 200G. It uses 850nm, 1310nm, CWDM or LWDM wavelength to transmit data. The QSFP56 optical transceiver module uses MPO as the optical interface, uses a 38-pin connector as the electrical interface, and uses PAM4 modulation technology to transmit more data on existing optical fibers and is suitable for ultra-large-scale data center networks.
Currently, there are two main types of 200G optical modules: 200G QSFP56 and 200G QSFP-DD. Both are designed for high-performance computing and data centers, and both are backwards compatible with earlier QSFP versions including QSFP28.
The difference between the two is mainly reflected in different modulation technologies. NRZ and PAM4 are two different types of digital modulation technologies. NRZ stands for non-return to zero code, and its other name is PAM2. A modulation method with two voltage levels representing logic 0 and logic 1, PAM4 pulse amplitude modulation technology uses four voltage levels to represent four combinations of two-bit logic 11, 10, 01 and 00. As a result, the transmission speed of PAM4 signals is twice that of traditional NRZ signals.
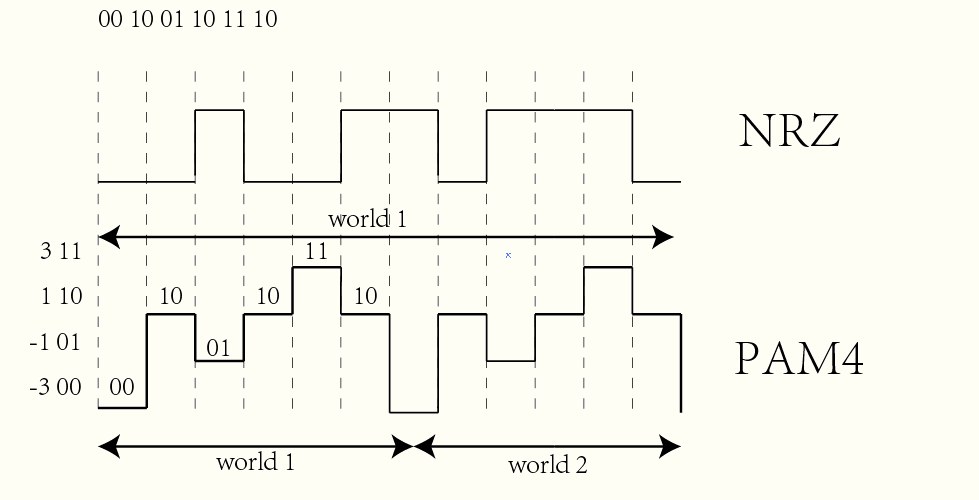
The main advantage of PAM4 over NRZ is faster transmission speed. Although NRZ modulation is not fast enough, NRZ (200G) has the advantages of lower power consumption, lower latency and easy deployment. 200G NRZ enables low-cost interconnect solutions within the data center.
QSFP56 is specially designed to meet the needs of 200G applications, but its technical architecture does not support direct upgrade to network environments with 400G and above rates. In contrast, QSFP-DD is compatible with both 200G and 400G rate versions, and allows users to gradually upgrade as needed, with greater scalability and flexibility.
In terms of modulation method, QSFP56 uses PAM4 technology, while QSFP-DD usually uses NRZ modulation when achieving 200G rate.
In terms of channel configuration, QSFP56 only needs 4 channels to complete 200G data transmission. Compared with QSFP-DD, which requires 8 channels, it has more advantages in terms of optical fiber cost and link loss.
In terms of price, the price of QSFP-DD is about 15% to 30% higher than that of QSFP56. It is worth noting that if current network equipment does not generally support QSFP-DD, it may be more economical to choose QSFP56. However, if you have sufficient budget and focus on future network expansion and performance optimization, QSFP-DD fiber optic transceiver is an ideal choice for easier subsequent upgrades.
Ensuring interoperability between optical transceiver modules and host devices is of utmost importance in optical network systems. The 200G QSFP56 optical transceiver module serves as a vital component, enabling the efficient transmission and reception of optical signals while converting them to electrical signals for seamless communication between switches. At UnitekFiber, our optical transceiver modules undergo rigorous testing to guarantee compatibility and flawless operation across various multi-brand switch environments. This testing process ensures that our optical transceiver modules can be confidently integrated into different switch systems, providing reliable and high-performance connectivity within optical networks.
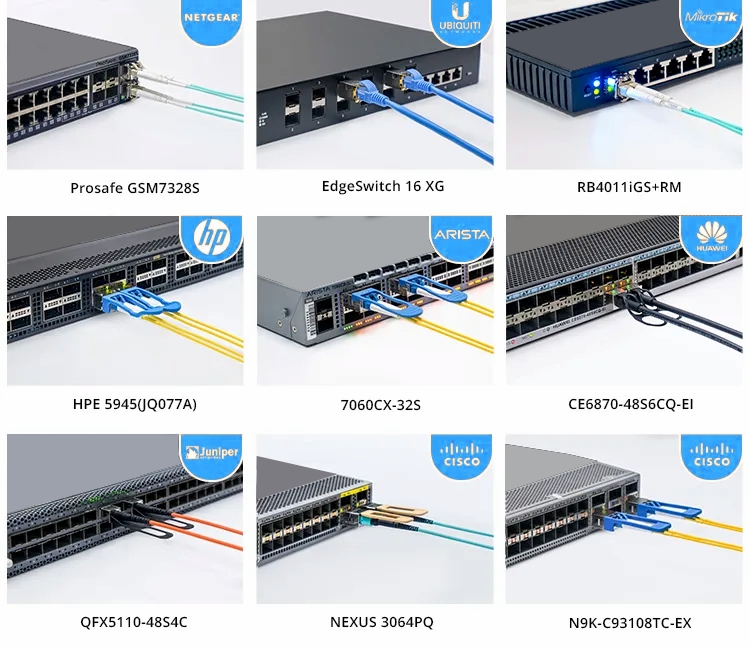

200G QSFP56 optical transceiver offer backward compatibility with QSFP+ and QSFP28 optical transceivers, allowing for a smooth integration and migration process within existing network infrastructures. This compatibility enables the reuse of QSFP+ and QSFP28 optical transceivers, supports multi-speed operation, ensures interoperability, and provides a flexible upgrade path for evolving network requirements. With 200G QSFP56 optical transceiver, network operators can leverage their existing infrastructure while gradually transitioning to higher speeds and enhanced performance.
The 200G QSFP56 optical transceiver module is an active component used in fiber optic communication networks. It transmits and receives data at a rate of 200 Gigabits per second over optical fibers.
The QSFP56-SR4-200G is compatible with both the IB HDR Switches MQM8790-HS2F and the MQM8700-HS2F.
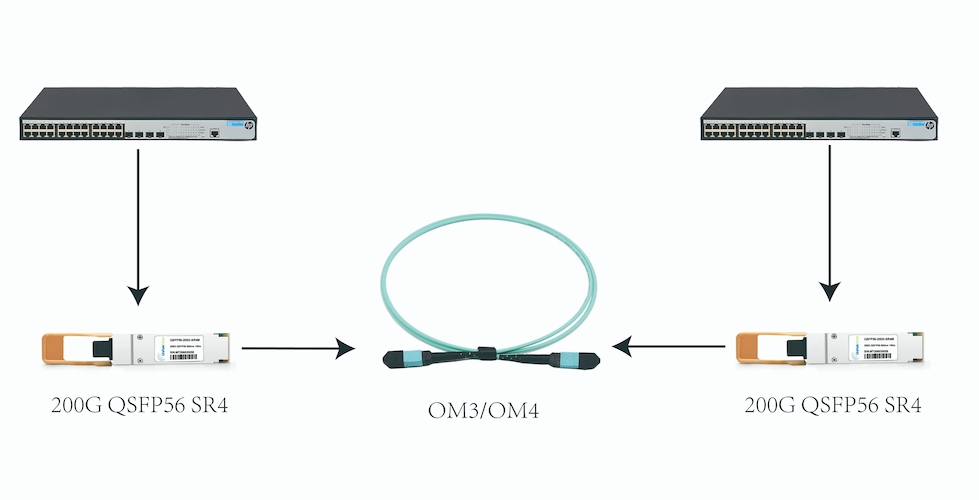
The 200G SR4 has the same interface type as the 100G SR4, allowing for a simple upgrade from 100G to 200G without changing the fiber type.
The interface of the QSFP56 200G SR4 transceiver needs to be connected with multimode MTP/MPO-12 patch cables.
Yes, please send inquiry to sales@unitekfiber.com so that we can have a detailed discussion.
We were looking for a product to replace our 15M 200G AOC cable and the techs at NADDOD recommended the 200G QSFP56 SR4, a module that helps us connect to longer distances, which is perfect.
This module has very good performance and stability, and we think this module is also very reasonably priced and cost effective.
The 200G optical modules are very compatible with a wide range of devices. This allows us to upgrade equipment or expand networks without worrying about compatibility issues.
The data transfer speeds are exceptional, allowing us to handle large volumes of data without any lag. This 200g optical QSFP56 transceiver is reliable, efficient, and delivers outstanding performance.
The 200g QSFP56 transceiver module delivers exceptional performance and ensures smooth communication between our network devices.