In the deployment of 10G networks, selecting the right transmission medium is crucial for ensuring network performance and reliability. This article will provide a comprehensive comparison of 10G DAC (Direct Attach Copper Cable) high-speed cables and 10G AOC (Active Optical Cable), helping you make an informed choice.
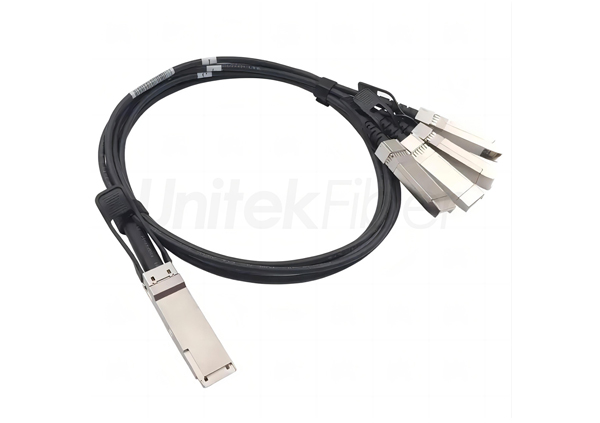
A 10G DAC high-speed cable (Direct Attach Cable) consists of a duplex copper cable with SFP+ connectors at both ends, and is usually used to connect devices in a rack. DAC cables are classified as either passive or active, with passive DACs containing no electronics, and active DACs containing electronics inside the connectors to enhance the signal.
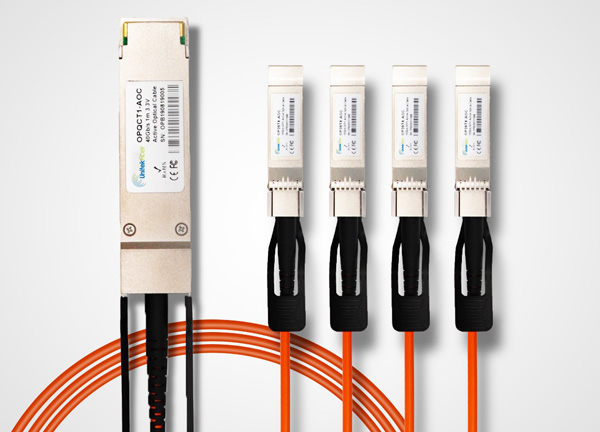
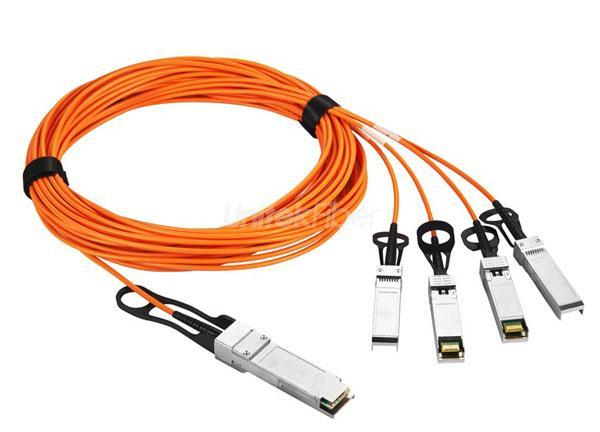
The 10G AOC active optical cable (Active Optical Cable) consists of a multimode fiber with SFP+ connectors at both ends and requires an external power supply for optical/electrical signal conversion. AOC cables are suitable for connecting between racks in data centers, especially when the distance exceeds the maximum transmission distance of the DAC cable.
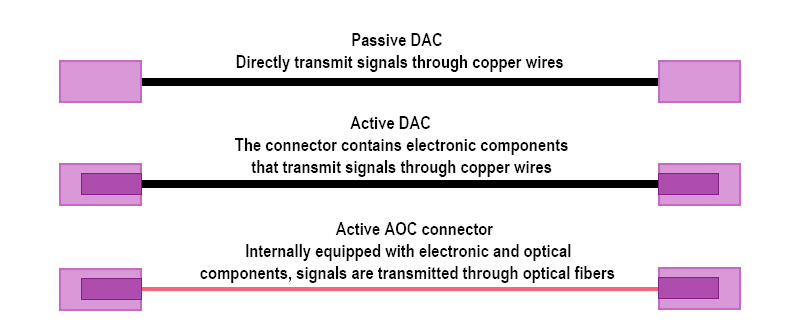
10G AOC is made from optical fiber material, which does not conduct electricity, making it immune to electromagnetic interference. This makes it suitable for environments with high electromagnetic interference. In contrast, 10G DAC cables contain copper, making them susceptible to such interference.
The power consumption of 10G DAC cable is typically under 1W, while passive DACs have even lower consumption that is nearly negligible. Low power consumption means reduced heat generation, allowing DAC cables to operate effectively across a broader temperature range. In comparison, 10G AOC cables have slightly higher power consumption, usually between 1-2W.
10G AOC cables can transmit data over distances of up to 100 meters, whereas 10G DAC cables have a shorter range; passive DACs can reach a maximum of 7 meters, and active DACs can go up to 10 meters. Therefore, for longer connections, AOC fiber optic cables are a more appropriate choice.
From a cost perspective, 10G DAC cables are generally less expensive than 10G AOC cables. This is because DAC cables have fewer internal components, a simpler structure, and copper material costs less than optical fiber. Thus, when deploying short-distance networks in large data centers, choosing DAC cables will save more costs.
10G DAC High-speed Cable: suitable for connecting servers to switches, especially in the same rack or short distance scenarios.

10G AOC Active Optical Cable: suitable for inter-rack connections, especially in data centers or environments with large electromagnetic interference.
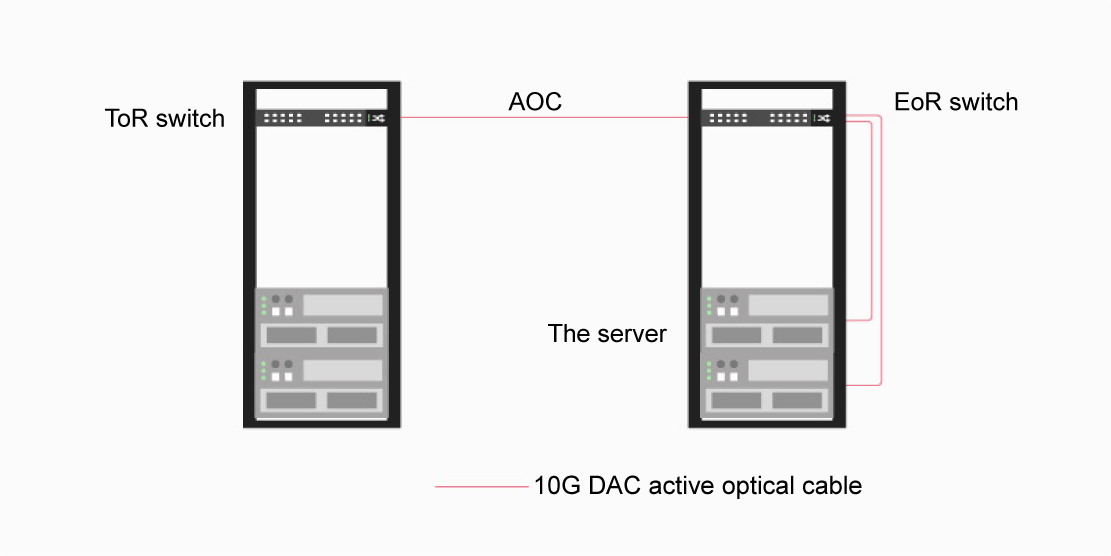
When choosing a 10G networking cabling solution, it’s essential to consider factors such as the application environment, cabling space, distance, power consumption, and budget. For short-distance transmission and cost-sensitive scenarios, 10G DAC cables are an ideal choice. Conversely, for long-distance transmission or electromagnetic interference environment, 10G AOC active fiber optic cable is more suitable.
During actual deployment, it is also important to consider cable compatibility, network equipment configuration, and the need for future network expansion. By carefully planning and selecting the right options, you can ensure high performance and reliability for your 10G network while keeping costs within a reasonable range.
UnitekFiber is a manufacturer focusing on high-performance optical modules, and its AOC (Active Optical Cable) and DAC (High-speed Cable) are widely used in a variety of application scenarios, such as data centers and communication networks. Let's take a deeper look at these two types of cables:
AOC consists of multimode fiber and SFP+ or QSFP+ connectors at both ends.
It requires an external power source to convert optical signals to electrical signals.
AOC is suitable for connections between racks in data centers, especially when the distance exceeds the maximum transmission range of DAC cables.
High-Speed Transmission: Supports data transfer speeds of up to 400 Gbps.
Electromagnetic Interference Resistance: Immune to electromagnetic interference, making it suitable for environments with high EMI.
DAC consists of twinax copper cable with SFP+ or QSFP+ connectors at both ends.
It is used for connecting devices within the same rack, such as servers to switches.
Cost-Effective: Its simple structure makes it less expensive.
Low Power Consumption: Typically under 1W, generating minimal heat.
Transmission Distance:
AOC is suitable for long-distance connections, with a maximum transmission range of up to 100 meters.
DAC cables are ideal for short-distance connections, generally with a maximum range of around 10 meters.
The choice between AOC and DAC depends on specific application needs and environmental conditions.
For longer distances and environments with significant electromagnetic interference, AOC is the better choice.
For short-distance transmission where cost is a concern, DAC cables are the ideal solution.



