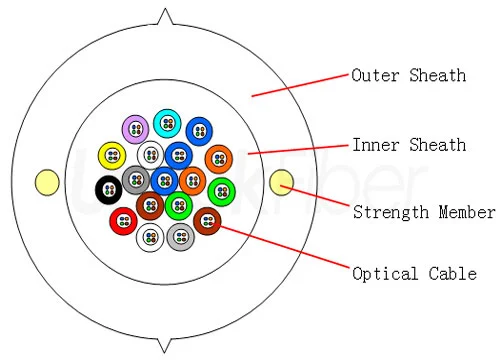
Anti-electric corrosion mechanism of ADSS optical cable
There is a high-voltage induction electric field around the high-voltage overhead transmission lines, especially the gradient of the high-voltage induction electric field near the poles and towers, and the high-voltage induction electric field has strong electrical corrosion on the optical cable. To set up optical cables around overhead transmission lines, ADSS optical cables with AT and PE polyethylene materials as the outer sheath must be used with electrical corrosion resistance.
AT outer sheath is suitable for the environment of high-voltage induction electric field ≤20KV/m, and is generally used for overhead power lines of 110KV and above. PE outer sheath is suitable for s12KV/m high-voltage induction electric field environment, generally used in 35KV and below overhead power lines.
The main technical parameters of ADSS optical cable
The ADSS optical cable works in a long-span two-point support (usually hundreds of meters, or even more than 1 km) in an overhead state, which is completely different from the traditional concept of "overhead" (the post and telecommunications standard overhead suspension wire hooking program, an average of 0.4 meters for the optical cable There is 1 fulcrum). Therefore, the main parameters of ADSS optical cable are basically the same as the participation of electric overhead lines.
Maximum allowable tension
The maximum allowable use tension (MAT/MOTS) refers to the tension that the optical cable is subjected to when the total load is calculated theoretically under the design weather conditions. Under this tension, the fiber strain should be <0.05% (stranded) and ≤0.1% (central tube) without additional attenuation. In layman's terms, the excess length of the optical fiber has just been "eaten" at this control value. According to this parameter, meteorological conditions and the controlled sag, the allowable span of the optical cable can be calculated under this condition. Therefore, MAT is an important basis for the calculation of sag-tension-span, and it is also an important evidence for characterizing the stress-strain characteristics of ADSS optical cables.

Rated resistance strength
Rated tensile strength (UTS/RTS) is also called ultimate tensile strength or breaking force, which refers to the calculated value of the sum of the strength of the load-bearing section (mainly counted as spinning). The actual breaking force should be greater than or equal to 95% of the calculated value (the breaking of any element in the optical cable is judged as cable breaking). This parameter is not optional, and many control values are related to it (such as tower strength, tensile hardware, anti-vibration measures, etc.). For fiber optic cable professionals, if the ratio of RTS/MAT (equivalent to the safety factor K of overhead lines) is not appropriate, that is, a lot of spun fibers are used and the available fiber strain range is very narrow, the economic/technical performance ratio is very poor. Therefore, attention must be paid to this parameter. Generally, MAT is approximately equivalent to 40% RTS.
Average annual stress
The annual average stress (EDS) is sometimes called the daily average stress. It refers to the tension of the optical cable under theoretically calculated load under no wind, no ice and annual average temperature. It can be considered as the average tension of the ADSS during long-term operation ((should ) Force. EDS is generally (16~20)%RTS should not be greater than 20% of the rated break. Under this tension, the optical fiber should have no strain and no additional attenuation, that is, very stable. EDS is the fatigue aging parameter of the optical cable at the same time, according to this parameter determines the anti-vibration design of the optical cable.
Ultimate operating tension
Ultimate operating tension (UES), also known as special use tension, refers to the maximum tension of the optical cable that may exceed the design load during the effective life of the optical cable. It means that the optical cable allows short-term overload, and the optical fiber can withstand strain within a limited allowable range. Generally, the UES should be >60% RTS. Under this tension, fiber strain <0.5% (central tube) and <0.35% (layer stranding), the fiber will have additional attenuation, but after the tension is relieved, the fiber should return to normal. This parameter guarantees the reliable operation of the ADSS optical cable during its lifetime.
ADSS optical cable is fully self-supporting and requires good mechanical properties. For optical cable manufacturers, it is mainly ensured by adding aramid yarn. When manufacturing the optical cable, first calculate the mechanical strength requirements of the optical cable according to the span of the power line, the sag of the optical cable, climatic conditions, icing, etc., and then calculate the amount of aramid yarn used.
For the design of optical cable lines in the power sector, the mechanical strength of the optical cable can mainly be shown by the tensile window (the data change window between the force extension of the optical cable and the strain of the optical cable). The large span requires the ADSS optical cable to have a larger tensile window. , But this index is too big to cause the microbend loss of the optical fiber. Practice shows that it is more appropriate to control it at 0.8%.
Since the design life of the ADSS optical cable exceeds 20 years, it is necessary to consider the surface of the optical cable during long-term use, which will increase the load.
UnitekFiber produces optical fiber indoor/outdoor cables, optical patch panels, fiber cable assembles etc. At the same time, it also produces optical transceiver modules, which can provide With different package types, transmission distance and transmission rate, it also has the characteristics of stable performance and strong compatibility. If you need any support,don't hesitate to contact us sales@unitekfiber.com.