When it comes to fiber optic cable, there are two primary types that are commonly used: gel fiber optic cable and dry fiber optic cable. These variations differ in terms of their construction and the materials used within them. In this article, we will explore the differences between gel fiber optic cable and dry fiber optic cable, helping you understand their unique characteristics and guiding you towards choosing the right option for your specific needs.
Gel Fiber Cable:
Construction
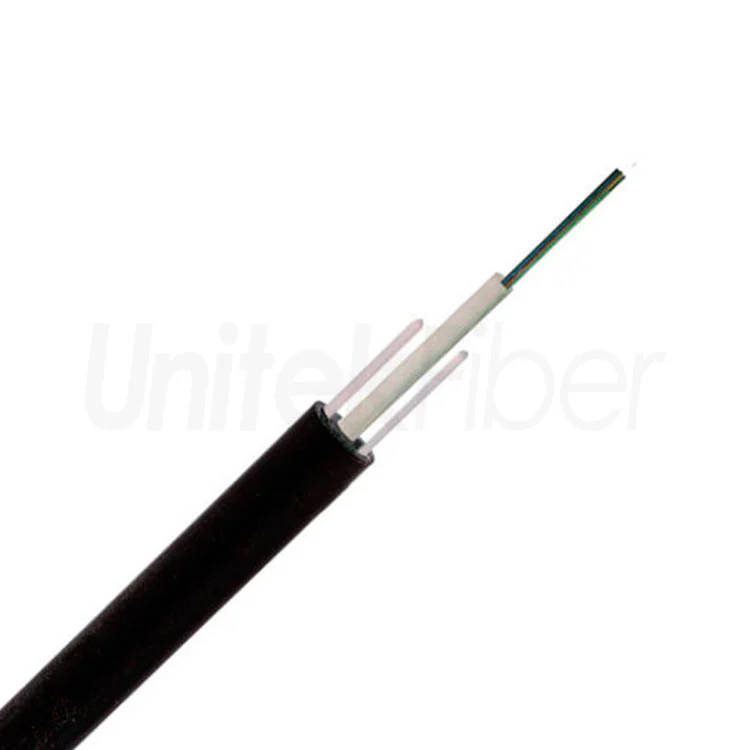
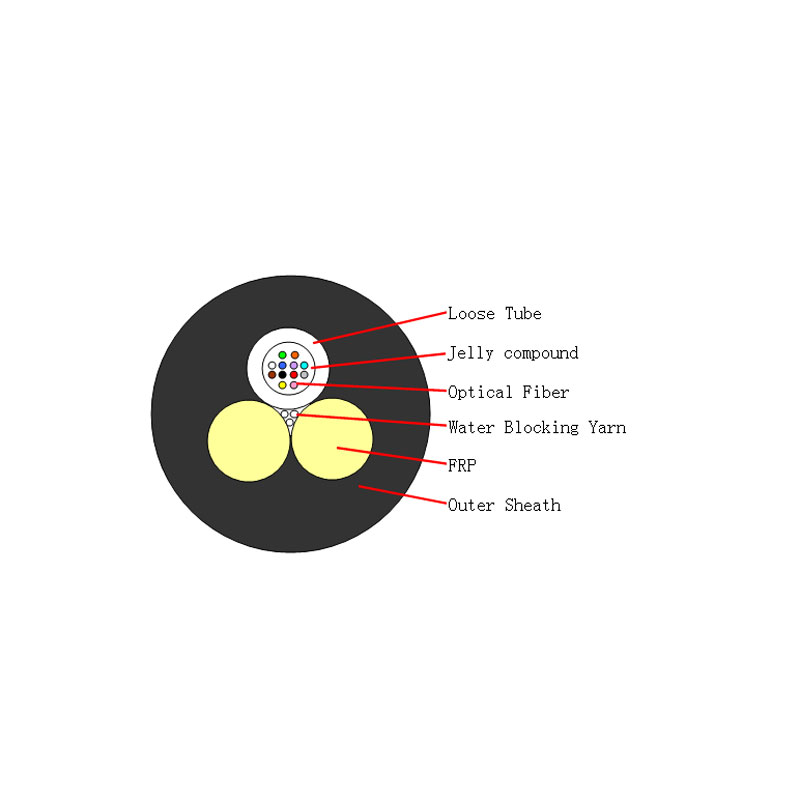
Gel fiber optic cable, also known as filled fiber optic cable, are designed with a gel-filled tube surrounding the individual optic fibers. This gel serves multiple purposes, including moisture protection, mechanical stress absorption, and enhancement of signal transmission, as discussed in our previous blog post.
Moisture Protection
The primary advantage of gel fiber optic cable is their superior resistance to moisture. The gel filling prevents moisture ingress, protecting the delicate optic fibers from degradation and maintaining optimal performance. This makes gel fiber optic cable particularly suitable for outdoor or harsh environments where exposure to moisture is a concern.
Ease of Handling
One drawback of gel fiber optic cable is their handling complexity. As the gel makes the optical cable more flexible, it can be messy and difficult to work with during installations. The gel requires careful handling and may need to be cleaned from the optic fibers before splicing or connecting.
Dry Fiber Cable:
Construction
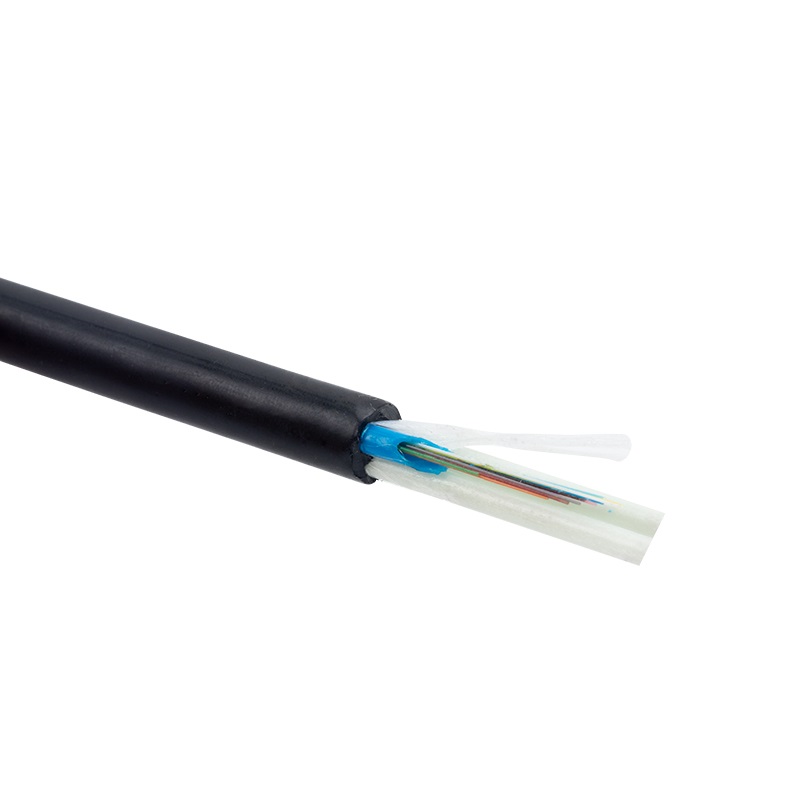
In contrast to gel fiber optic cable, dry fiber optic cable do not contain any gel-filled tubes. Instead, they rely on various dry materials to protect the optic fibers. These materials can include coatings, tapes, or water-blocking yarns, which offer mechanical protection and prevent moisture ingress.
Moisture Protection
While dry fiber optic cable offer some degree of moisture protection, they are generally less resistant to moisture compared to gel fiber optic cable. Although the dry materials used in their construction provide adequate protection against most environmental conditions, they may not be suitable for extremely wet or humid environments.
Handling and Ease of Installation
Dry fiber cables are generally easier to handle and install compared to gel fiber optic cable. Without the gel filling, they are less messy and can be bent or routed with greater flexibility. This makes them a preferred choice in applications where ease of handling and installation efficiency are critical factors.

Conclusion
Both gel fiber optic cable and dry fiber optic cable have their own advantages and considerations. Understanding the differences between these two options is crucial in selecting the right optical cable for your specific application. Whether you prioritize moisture protection or ease of handling, make an informed decision based on the environmental conditions and installation requirements. By choosing the appropriate optical cable, you can ensure optimal performance and longevity of your fiber optic network.
As a leading fiber optic supplier, UnitekFiber is dedicated to providing high-quality fiber optic cable like pre-terminated direct burial fiber, mpo to lc breakout cable, MPO to SC breakout cable, and outdoor fiber patch cable that meet your specific requirements. For more detailed information, please visit our website at www.unitekfiber.com. We look forward to supporting you with our reliable and efficient fiber optic solutions.