While single mode fiber (SMF) and multimode fiber (MMF) optic cable types are extensively utilized in various applications, the dissimilarities between these two fiber optic cable types can often be perplexing. Understanding the differences between these two types is crucial for selecting the appropriate fiber optic cable for specific applications. In this blog, we UnitekFiber will explore the dissimilarities between multimode fiber and single mode fiber and discuss their respective advantages and disadvantages.
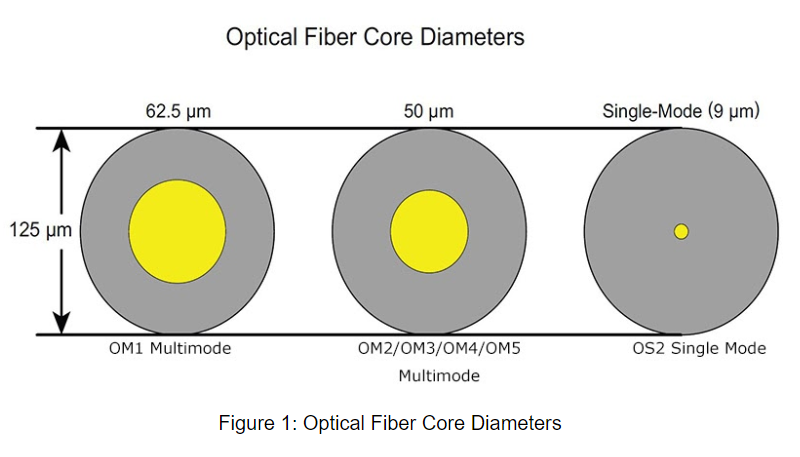
Multimode fiber has a larger core diameter, typically 50µm or 62.5µm, allowing multiple light rays to propagate simultaneously. These different modes take various paths through the fiber optic cable, resulting in a phenomenon called modal dispersion. As a consequence, multimode fiber is suitable for shorter distances, typically up to a few hundred meters.
Single mode fiber has a smaller fiber core diameter, usually 9µm, which allows only one mode of light to propagate. As a result, single mode fiber experiences minimal dispersion, making it ideal for long-distance transmissions that can span tens or even hundreds of kilometers.
Single mode fiber is commonly used for long-distance transmission in telecommunications networks, while multimode fiber is often utilized in data centers and shorter distance applications like local area networks (LANs). Single mode fiber enables high-speed and low-loss transmission over long distances, making it ideal for intercity and transcontinental communication. On the other hand, multimode fiber has a larger core size that allows for easier coupling with lower-cost light sources, making it suitable for short-reach applications such as connecting servers and networking equipment within a data center.
The attenuation between single mode fiber and multimode fiber can vary depending on several factors, including the optical fiber cable type and wavelength of light used.
In general, single mode fiber has lower attenuation compared to multimode fiber. The attenuation values for single mode fiber and multimode fiber are typically specified in decibels per kilometer (dB/km). The single mode fiber typically has attenuation values ranging from 0.2 dB/km to 0.5 dB/km, depending on the wavelength used (common wavelengths include 1310nm and 1550nm). The exact attenuation can vary based on the modal bandwidth and the specific type of multimode fiber (such as OM3, OM4 and OM5). Typical attenuation values for multimode fiber range from 2 dB/km to 4 dB/km for 850nm wavelength.
Understanding the differences between multimode fiber and single mode fiber is essential for selecting the appropriate fiber optic cable for specific purposes. While multimode fiber suits shorter distances and is cost-effective, single mode fiber excels in long-distance, high-bandwidth applications. Depending on the requirements of your communication network, you can choose the suitable fiber optic cable solution to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
UnitekFiber as a professional manufacturer focusing on fiber optic technology, In addition to providing high quality single mode or multimode fiber optic cables, fiber optic patch cord, we also produce optical transceiver modules and MPO/MTP patch panel. Trust UnitekFiber to supply innovation and wholesale price fiber optic product for your network needs. For more detailed information, please visit our website at www.unitekfiber.com.